Vocabulary acquisition is an essential pathway to third grade literacy.
Three Tiers of Vocabulary and Education
by Thaashida L. Hutton, M.S., CCC-SLP
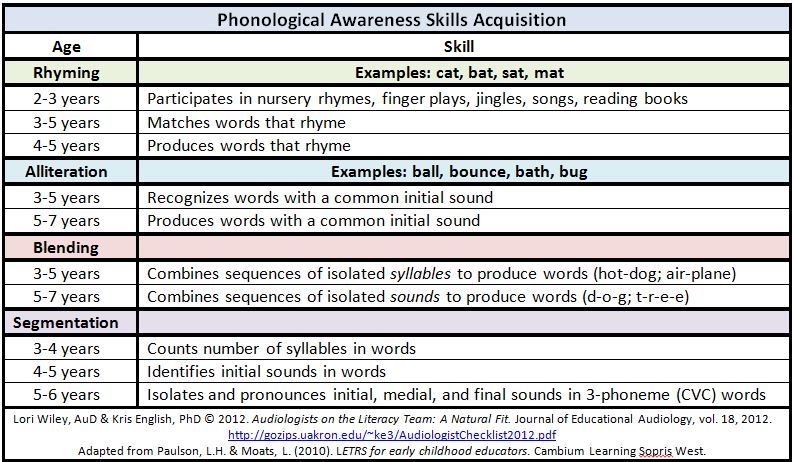
Vocabulary consists of the words we understand when we hear or read them (receptive vocabulary) and words we speak or write (expressivevocabulary). We build vocabulary by picking up words that we read or hearand through direct instruction from teachers or other professionals. Knowing a variety of words is important for language development and reading comprehension. A limited vocabulary is usually a “red flag,” indicating a possible language learning disability and reduced literacy skills. Most children begin first grade with about 6,000 words of spoken vocabulary. They will learn 3,000 more words per year through third grade.However, not all words have equal importance in language instruction. So,how do we know which words we need to teach? We consider three types of vocabulary words—three tiers of vocabulary—for teaching and assessing word knowledge. A word’s frequency of use, complexity, and meaning determines into which tier it will fall. Those with mature vocabularies and age-appropriate literacy skills understand and use words from all three tiers. This handout discusses the three tiers of vocabulary,
Tier 1—Basic Vocabulary, Tier 2—High Frequency/Multiple Meaning, and Tier 3—SubjectRelated
TIER 1: BASIC VOCABULARY
These words rarely require direct instruction and typically do not have multiple meanings. Sight words, nouns, verbs, adjectives, and early reading wordsoccur at this level. Examples of tier one words are: book, girl, sad, run, dog,and orange. There about 8,000 word families in English included in tier one.
TIER 2: HIGH FREQUENCY/MULTIPLE MEANING
Tier two consists of high frequency words that occur across a variety of domains. That is, these words occur often in mature language situations such as adult conversations and literature, and therefore strongly influence speaking and reading.
Following is a list of standards for tier two words:
- Important for reading comprehension
- Characteristic of mature language users
- Contain multiple meanings
- Increased descriptive vocabulary (words that are used across a variety of environments allow students to describe concepts in (generalization) a detailed manner)
Tier two words are the most important words for direct instruction because they are good indicators of a student’s progress through school.
Examples of tier two words are: . There are about 7,000 word families in English (or 700 per year) in tier two.
TIER 3: LOW-FREQUENCY WORDS (Specific Domain)
Domains include subjects in school, hobbies, occupations, geographic regions, technology, weather, etc. We usually learn these words when a specific need arises, such as learning amino acid during achemistry lesson. Examples of tier three words are: ** . The remaining 400,000 words in English fall in this tier. It important to remember that tier two and three words are not all clear-cut in their tierclassification. There is more than one way to select the words. Word knowledge is subject to personal experience.
The MacArthur Bates CDI {Communicative Development Inventory}
The vocabulary portion consists of 680 words organized into 22 semantic categories (e.g., animals, toys, and food) and syntactic categories including nouns, verbs, and adjectives